CLEVIPREX® (clevidipine) demonstrated safety in multiple clinical trials
CLEVIPREX clinical development program
The safety and tolerability of CLEVIPREX have been evaluated in multiple clinical trials and treatment settings.1-5
*Clinical development included 19 studies, but CLEVIPREX was evaluated in 15 studies in hypertensive patients.
CLEVIPREX Safety Profile
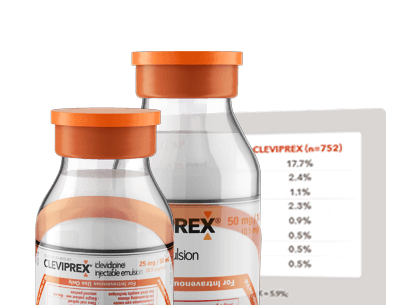
CLEVIPREX safety profile in placebo-controlled efficacy studies
See common AEs in clinical trials of CLEVIPREX in patients with pre- and postoperative hypertension (ESCAPE-1 and ESCAPE-2 studies, respectively).
CLEVIPREX safety profile in active-controlled safety studies
See how CLEVIPREX performed in 3 open-label studies in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.
Common AEs by day 7 or discharge vs placebo in the perioperative setting
*In ESCAPE-1 (preoperative), AEs reported by ≥5.7% of CLEVIPREX-treated patients from study drug initiation until hospital discharge or 7 days.
†In ESCAPE-2 (postoperative), AEs reported by ≥10% of CLEVIPREX-treated patients from study drug initiation until hospital discharge or 7 days.
ESCAPE-1 and ESCAPE-22,3 Study Design
These results are from 2 double-blind, randomized, parallel, placebo-controlled, multicenter trials of cardiac surgery patients—preoperative use (N=105) and postoperative use (N=110), respectively. Patients were undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting with or without valve replacement. The primary endpoint was the incidence of treatment failure, defined as the inability to decrease SBP by ≥15% from baseline or the discontinuation of study treatment for any reason within the 30 minutes after study drug initiation.
Low-volume dosing option6
See how CLEVIPREX compared against another BP-lowering agent in the postoperative setting.

The ECLIPSE Study Design1
Three parallel, prospective, randomized, open-label studies in patients undergoing cardiac surgery at 61 medical centers (N=1506).
- Perioperative setting: CLEVIPREX (n=268) vs nitroglycerin (n=278)
- Perioperative setting: CLEVIPREX (n=296) vs sodium nitroprusside (n=283)
- Postoperative setting: CLEVIPREX (n=188) vs nicardipine (n=193)
![]() Image description
Image description
Primary Endpoint: Safety, defined as incidence of death, myocardial infarction, stroke, or renal dysfunction at 30 days vs comparators. Study was not powered for noninferiority or superiority.
Secondary Endpoint: Efficacy by measuring the magnitude and duration of BP excursions above or below a predefined SBP range vs comparators.
*Numbers for safety population.
Incidence of serious AEs in ECLIPSE trials1,6
The AEs observed within 1 hour of the end of infusion were similar in patients who received CLEVIPREX and those who received comparator agents.
The ability to differentiate the AE profile between treatments was limited6
- Many AEs were associated with the operative procedure6
- Relatively few AEs were plausibly related to CLEVIPREX and the comparators6
- AEs observed within 1 hour of the end of infusion were similar between patients who received CLEVIPREX and those who received comparators1,6
- No AEs were >2% more common with CLEVIPREX than with the average of all the comparators6
Onset within minutes6
CLEVIPREX has a titratable, fast onset of action and short half-life.